Super Coding Addict
Ch06. 배열(2) 본문
< 다차원 배열 >
* 다차원 배열
- 2차원 이상의 배열
- 지도, 게임, 평면, 공간 구현시 사용

| arr[0][0] | arr[0][1] | arr[0][2] |
| arr[1][0] | arr[1][1] | arr[1][2] |
- 메모리에는 일차원으로 만들어지지만! 논리적으로는 이런식으로 구성...
- 예제 : 2차원 배열
[ TwoDimesion 클래스 ]
package array;
public class TwoDimension {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = { {1,2,3}, {4,5,6} };
System.out.println(arr.length); //2 (행의 갯수)
System.out.println(arr[0].length); //3
System.out.println(arr[1].length); //3
//이중 for문으로 요소들 꺼내기
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
--> 2중 for문으로 arr배열의 요소들을 찍으면 다음과 같은 결과가 나타남
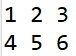
< ArrayList 사용하기 >
* ArrayList 클래스
- 객체배열을 사용하는 데 필요한 여러 메서드들이 구현되어 있음
- 예제
[ ArrayListTest 클래스 ]
package array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); //제네릭 타입
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) { //cf. 배열은 length --> 반드시 정해진 길이대로
String str = list.get(i);
System.out.println(str);
}
for(String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
--> ArrayList는 size()메서드를 배열의 length()처럼 쓴다.
배열의 경우 기존에 정해진 길이만큼 반복하는 한편(요소가 다 들어가 있지 않앋호), ArrayList는 들어가 있는 요소
갯수만큼만 반복!
--> 제네릭 타입으로 String으로 지정해주었기 때문에 (제네릭타입을 안쓰면 Object형임) 반복을 해서 꺼낼 때 따로
형변환을 할 필요가 없었음
참조 : ArrayList에 커서를 놓고 F1을 누르면 Help로 API 볼 수 있음
참조 : Ctrl + Shift + O를 누르면 import
- 예제 : 학생의 수강과목 학점 출력하기
--> 한 학생당 수강과목이 여러 개이므로, 수강과목을 위한 Subject 클래스를 새로 만들고 그 클래스를 타입으로 하는 ArrayList를 생성하여 각각의 Subject객체들을 생성한 후 넣어준다.
[ Subject 클래스 ]
package array;
public class Subject {
private String name;
private int score;
public Subject(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
[ Student 클래스 ]
package array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
int studentID;
String studentName;
ArrayList<Subject> subjectList;
public Student(int studentID, String studentName) {
this.studentID = studentID;
this.studentName = studentName;
subjectList = new ArrayList<Subject>();
}
public void addSubject(String name, int score) {
//ArrayList를 생성했다고 끝난 게 아니라, 매번 Subject 객체를 생성해줘야 함
//String형인 경우는 따로 생성하지 않고 쓸 수 있었지만
Subject subject = new Subject(name, score);
subjectList.add(subject);
}
public void showStudentInfo() {
int total = 0;
for( Subject subject : subjectList ) {
total += subject.getScore();
System.out.println(studentName + " 학생의 " + subject.getName() + " 과목의 성적은"
+ subject.getScore() + "점 입니다.");
}
System.out.println(studentName + " 학생의 총점은 " + total + "점 입니다.");
}
}
[ StudentTest 클래스 - 메인 ]
package array;
public class StudemTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentLee = new Student(1001, "Lee");
studentLee.addSubject("국어", 100);
studentLee.addSubject("수학", 90);
Student studentKim = new Student(1002, "Kim");
studentKim.addSubject("국어", 100);
studentKim.addSubject("국어", 90);
studentKim.addSubject("영어", 80);
studentLee.showStudentInfo();
System.out.println("===================================");
studentKim.showStudentInfo();
}
}
< 코딩해 보세요 >


* 내 코드
< Student 클래스 >
package book;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
int studentID;
String studentName;
ArrayList<Book> bookList;
public Student(int studentID, String studentName) {
this.studentID = studentID;
this.studentName = studentName;
bookList = new ArrayList<Book>();
}
public void readBook(String bookName) {
Book book = new Book(bookName);
bookList.add(book);
}
public void showStudentInfo() {
System.out.print(studentName + " 학생이 읽은 책은 : ");
for( Book book : bookList ) {
System.out.print(book.getBookName() + " ");
}
System.out.print(" 입니다");
}
}
< Book 클래스 >
package book;
public class Book {
String bookName;
public Book (String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
public String getBookName() {
return bookName;
}
public void setBookName(String bookName) {
this.bookName = bookName;
}
}
< StudentTest 클래스 >
package book;
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentLee = new Student(1001, "Lee");
studentLee.readBook("태백산맥1");
studentLee.readBook("태백산맥2");
Student studentKim = new Student(1002, "Kim");
studentKim.readBook("토지1");
studentKim.readBook("토지2");
studentKim.readBook("토지3");
Student studentCho = new Student(1003, "Cho");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터1");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터2");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터3");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터4");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터5");
studentCho.readBook("해리포터6");
studentLee.showStudentInfo();
System.out.println();
studentKim.showStudentInfo();
System.out.println();
studentCho.showStudentInfo();
}
}
'JAVA 문법' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Ch12. 람다식 (1) (0) | 2021.02.06 |
|---|---|
| Ch07. 상속과 다형성 (1) (0) | 2021.01.22 |
| Ch06. 배열(1) (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| Ch05. 클래스와 객체(3) (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| Ch05. 클래스와 객체(2) (0) | 2021.01.19 |



