Super Coding Addict
Ch15. 자바 Thread 프로그래밍 (5) - multi-thread 프로그래밍 본문
* deadlock
- 2개 이상의 Thread가 서로 기다림
* wait()와 notify() 메서드
- wait() : 리소스는 한정적이므로 리소스가 유효하지 않을 때 다시 available할 때까지 thread가 non-runnable상태로 전환되어 대기 --> notify()가 호출될 때까지 기다림
- notify() : wait()하고 있는 하나의 thread를 runnable하게 깨운다 (but the oldest가 아니라, 아무 thread나 깨움!)
-. notifyAll() : wait()하고 있는 모든 thread를 깨움
--> notifyAll()이 더 권장됨, 모든 thread를 다 깨워서 서로 CPU 점유 경쟁을 하게한 후, non-runnable한 thread는 다시 잠들게 된다
==> 특정 thread가 통지를 받도록 제어할 수 없어 모두 깨운 후 schedular가 CPU를 할당하는 것이 공평
- 예제
# 책대여반납
-- FastLibrary 클래스
class FastLibrary{
public ArrayList<String> books = new ArrayList<String>();
public FastLibrary() { //생성자
books.add("태백산맥 1");
books.add("태백산맥 2");
books.add("태백산맥 3"); //리소스 한정적!
}
public synchronized String lendBook() throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
while(books.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting start");
wait(); //currentThread를 기다리게함
System.out.println(t.getName() + " waiting end");
}
String title = books.remove(0);
System.out.println(t.getName() + ":" + title + " lend");
return title;
}
public synchronized void returnBook(String title) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
books.add(title);
notifyAll();
System.out.println(t.getName() + ":" + title + "return");
}
}
-- Student 클래스
class Student extends Thread{
public void run() {
try {
String title = LibraryMain.library.lendBook();
if ( title == null) return; //책을 못빌리는 걸로 끝나게 됨
sleep(5000);
LibraryMain.library.returnBook(title);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-- LibraryMain 클래스
public class LibraryMain {
public static FastLibrary library = new FastLibrary();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student std1 = new Student();
Student std2 = new Student();
Student std3 = new Student();
Student std4 = new Student();
Student std5 = new Student();
Student std6 = new Student();
std1.start();
std2.start();
std3.start();
std4.start();
std5.start();
std6.start();
}
}
--> 책은 3권이지만 학생은 6명이기에 리소스인 책이 한정되어 있다
--> 따라서 책 3권이 대여가 되면, 한 권이 반납될 때 비로소 다른 1명이 책을 대여할 수 있게 된다
--> books.size() == 0일 때가 바로 책 3권이 모두 대여가 되었을 때이고, 이 때 wait() 메서드 호출로 thread를 non-runnable 상태로 만든다
--> 이 때 non-runnable상태인 학생 thread은 1개 이상일 수 있다
--> 책 1권이 반납되면 notifyAll() 메서드를 호출해 non-runnable 상태에 있는 thread들을 모두 깨우고 깨어난 thread들 중 랜덤하게 책을 대여해가면 다시 books.size() == 0이 되어 나머지 thread들은 non-runnable한 상태로 다시 빠지게 된다 (while문으로 반복을 걸어놓았음)
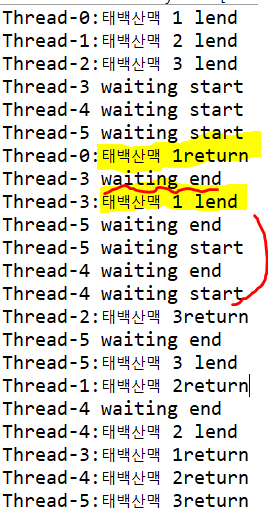
--> 결과를 살펴보면, 책 3권이 모두 대여가 되면 나머지 3명 학생들의 thread(3,4,5)는 wait()호출로 non-runnable한 상태에 빠지며, 태백산맥 1return과 동시에 notifyAll()로 thread(3,4,5)의 wait()가 끝이 났다가 태백산맥 1권이 다시 대여되어 대여할 책이 없게 되어 wait가 다시 시작되고 있음을 알 수 있다
'JAVA 문법' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Ch14. 자바 입출력 (2) (0) | 2021.02.16 |
|---|---|
| Ch14. 자바 입출력 (1) (0) | 2021.02.16 |
| Ch15. 자바 Thread 프로그래밍 (4) - multi-thread 프로그래밍 (0) | 2021.02.14 |
| Ch15. 자바 Thread 프로그래밍 (3) (0) | 2021.02.14 |
| Ch15. 자바 Thread 프로그래밍 (1) (0) | 2021.02.14 |




